Basic Concepts of Cell Biology: verschil tussen versies
| (4 tussenliggende versies door 2 gebruikers niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 2: | Regel 2: | ||
[[Categorie:msf]] | [[Categorie:msf]] | ||
=Information= | =Information= | ||
This course is mandatory for the | This course is mandatory for the master-na-master medsiche stralingsfysica. It is given in the first semester by three professors: | ||
==Prof. Veerle Baekelandt== | ==Prof. Veerle Baekelandt== | ||
| Regel 11: | Regel 11: | ||
==Prof. Hans Steenackers== | ==Prof. Hans Steenackers== | ||
Prof. Hans Steenackers ([mailto:hans.steenackers@kuleuven.be hans.steenackers@kuleuven.be]) changes his topic from year to year. In 2023-2024 he | Prof. Hans Steenackers ([mailto:hans.steenackers@kuleuven.be hans.steenackers@kuleuven.be]) changes his topic from year to year. In 2023-2024 he talked about cell energetics. You get the questions of his part beforehand so you can prepare yourself. | ||
==Good books== | ==Good books== | ||
| Regel 20: | Regel 20: | ||
=Exam questions= | =Exam questions= | ||
==2023-2024== | ==2023-2024== | ||
===26 January | ===26 January 2024=== | ||
'''Prof. Veerle Baekelandt''' | '''Prof. Veerle Baekelandt''' | ||
Explain briefly following terms: | Explain briefly the following terms: | ||
# Capsid | # Capsid | ||
# Voltage gated K channel | # Voltage-gated K channel | ||
Name in the following figures what you can see and how the figure is made. | Name in the following figures what you can see and how the figure is made. | ||
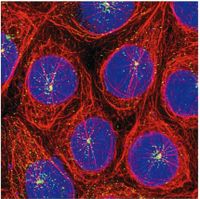
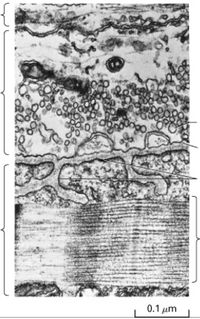
# [[Bestand:Basic-concepts-of-cell-biology 2024-01-26 1.jpeg|200px|||Figure 20.13 in the book]] | # [[Bestand:Basic-concepts-of-cell-biology 2024-01-26 1.jpeg|200px|||Figure 20.13 in the book]] | ||
| Regel 36: | Regel 36: | ||
'''Prof. Hans Steenackers''' | '''Prof. Hans Steenackers''' | ||
# Rubisco, which may be the most abundant protein on earth, plays a key role in the synthesis of carbohydrates in organisms that use photosynthesis. What is rubisco, where is it located, and what function does it serve? | # Rubisco, which may be the most abundant protein on earth, plays a key role in the synthesis of carbohydrates in organisms that use photosynthesis. What is rubisco, where is it located, and what function does it serve? | ||
# The Q cycle plays a major role in the electron transport chain of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. What is the function of the Q cycle, and how does it carry out this function? What electron transport components participate in the Q cycle in mitochondria, in purple bacteria, and in | # The Q cycle plays a major role in the electron transport chain of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. What is the function of the Q cycle, and how does it carry out this function? What electron transport components participate in the Q cycle in mitochondria, in purple bacteria, and chloroplasts? | ||
==2024-2025== | |||
===24 January 2025=== | |||
'''Prof. Joris Winderickx''' | |||
# Proteins are being matured while in the ER and the Golgi apparatus. Explain the post-translational protein modifications that can occur in these organelles and how proteins traffic from one to the other. | |||
# Explain briefly: | |||
## Leading and lagging strands | |||
## Coding and template DNA strands | |||
## Antiporter | |||
## V-class ion pump | |||
'''Prof. Hans Steenackers''' | |||
# (19.) Chloroplasts contain two photosystems. What is the function of each? For linear electron flow, diagram the flow of electrons from photon absorption to NADPH formation. What does the energy stored in the form of NADPH synthesize? | |||
# (9.) It is estimated that each electron pair donated by NADH leads to the synthesis of approximately three ATP molecules, whereas each electron pair donated by FADH2 leads to the synthesis of approximately two ATP molecules. What is the underlying reason for the difference in yield for electrons donated by FADH2 versus NADH? | |||
'''Prof. Veerle Baekelandt''' | |||
Name in the following figures what you can see and how the figure is made: | |||
# [Image of the structure of the centriole (from the lecture slides ''The eukaryotic cell'', p.69)] | |||
# [Image of the motor neutrons at neuromuscular junctions (from the lecture slides ''Signaling in nerve cells'', p.36)] | |||
# [Image of a deconvolution fluorescence microscopy macrophage cell (from ''Molecular Cell Biology'', fifth edition, Figure '''5-49''')] | |||
# Explain briefly: | |||
## capsid | |||
## voltage-gated K channel | |||
Huidige versie van 26 jan 2025 21:23
Information
This course is mandatory for the master-na-master medsiche stralingsfysica. It is given in the first semester by three professors:
Prof. Veerle Baekelandt
Prof. Veerle Baekelandt (veerle.baekelandt@kuleuven.be) will talk about the general structures inside the cell, eukaryotes, and prokaryotes, bacteria, and viruses. She will also talk about cell differentiation and communication, the cell cycle, and signaling in nerve cells.
Prof. Joris Winderickx
Prof. Joris Winderickx (joris.winderickx@kuleuven.be) will talk about DNA, RNA, regulation of gene transcription, proteins, protein sorting, vesicular transport, cell membrane transport and signaling at the cell surface.
Prof. Hans Steenackers
Prof. Hans Steenackers (hans.steenackers@kuleuven.be) changes his topic from year to year. In 2023-2024 he talked about cell energetics. You get the questions of his part beforehand so you can prepare yourself.
Good books
Books on which the professors bases their courses are:
- Molecular Cell Biology - H. Lodisch et al.
- Introduction to Genetic Analysis - A. Griffiths
Exam questions
2023-2024
26 January 2024
Prof. Veerle Baekelandt
Explain briefly the following terms:
- Capsid
- Voltage-gated K channel
Name in the following figures what you can see and how the figure is made.
Prof. Joris Winderickx
- Explain GPCR. What is the structure of GPCR? How can GPCR go to the correct location? Explain in your answer the cargo selection, vesicle formation, and membrane fusion. Draw a schematic process of the typical receptor workings of GPCR.
Prof. Hans Steenackers
- Rubisco, which may be the most abundant protein on earth, plays a key role in the synthesis of carbohydrates in organisms that use photosynthesis. What is rubisco, where is it located, and what function does it serve?
- The Q cycle plays a major role in the electron transport chain of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. What is the function of the Q cycle, and how does it carry out this function? What electron transport components participate in the Q cycle in mitochondria, in purple bacteria, and chloroplasts?
2024-2025
24 January 2025
Prof. Joris Winderickx
- Proteins are being matured while in the ER and the Golgi apparatus. Explain the post-translational protein modifications that can occur in these organelles and how proteins traffic from one to the other.
- Explain briefly:
- Leading and lagging strands
- Coding and template DNA strands
- Antiporter
- V-class ion pump
Prof. Hans Steenackers
- (19.) Chloroplasts contain two photosystems. What is the function of each? For linear electron flow, diagram the flow of electrons from photon absorption to NADPH formation. What does the energy stored in the form of NADPH synthesize?
- (9.) It is estimated that each electron pair donated by NADH leads to the synthesis of approximately three ATP molecules, whereas each electron pair donated by FADH2 leads to the synthesis of approximately two ATP molecules. What is the underlying reason for the difference in yield for electrons donated by FADH2 versus NADH?
Prof. Veerle Baekelandt Name in the following figures what you can see and how the figure is made:
- [Image of the structure of the centriole (from the lecture slides The eukaryotic cell, p.69)]
- [Image of the motor neutrons at neuromuscular junctions (from the lecture slides Signaling in nerve cells, p.36)]
- [Image of a deconvolution fluorescence microscopy macrophage cell (from Molecular Cell Biology, fifth edition, Figure 5-49)]
- Explain briefly:
- capsid
- voltage-gated K channel